With apologies for borrowing from the late great Mark Twain… our latest blog outlines our thoughts in relation to reports of the alleged ‘death’ of ESG, including looking into the history of ESG, where some of these claims are coming from, the motivation behind them, and where things stand as we look forward.
A timeline of ESG, and how its meaning has changed
Though forms of socially responsible investing have existed as early as the 1750s when the Quakers prohibited members from engaging in the slave trade, the term ‘ESG’ (standing of course for ‘Environmental, Social and Governance’) wasn’t coined until 2004, when the United Nations released a report called Who Cares Wins. Following its introduction the acronym quickly went on to gain more and more popularity, as investors increasingly sought for a way to express their sustainability concerns through their investment choices.
This momentum only grew throughout the 2010s as the public became more aware of the climate crisis, and other worsening environmental crises the world faces. As retail investors began to witness increasingly violent weather patterns and alarming record temperatures, demand for ‘sustainable’, ‘ethical’, and ESG investment opportunities exploded.
This can be seen through the below chart, which shows the growth in AUM and number of sustainable funds over the decade from 2010 to 2020.
Number and AUM of sustainable funds, 2010-2020
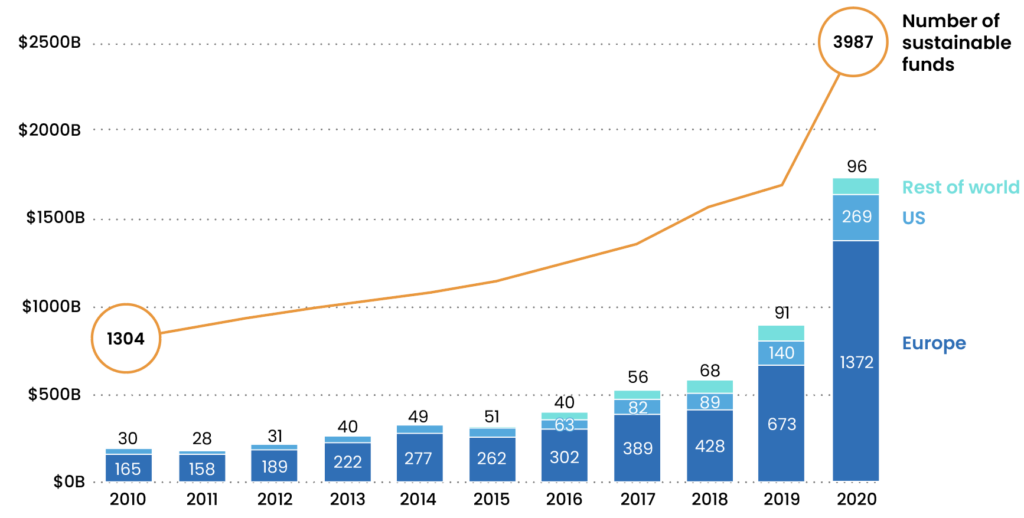
Source: UNCTAD based on Morningstar and TrackInsight data. Note: Number of funds do not include funds that were liquidated.
Naturally, these ESG solutions looked well placed to be high performers (and many have been) with the ever-growing intensity of government action, most notably in Paris in 2015 and Glasgow in 2021, and public sentiment. For the last decade markets have placed large bets on ESG-related assets, and the idea that their market prices reflect the overwhelming consensus that sustainability will be humanity’s priority throughout the 21st century.
Why some people are now claiming that ESG is ‘dead’
It feels strange therefore that some analysts have begun to state recently that ESG is ‘dead’ or ‘over’. For example, Fabiana Fedeli, CIO for Equities and Sustainability at M&G Investments, recently told the Financial Times: “I feel the ESG Hype Cycle is over. I think we’re at a point of disillusionment”. Why is this? The climate crisis certainly hasn’t gone anywhere in the last year or two (quite the opposite), nor has there been a large-scale shift in public opinion on matters related to social issues or corporate governance. Governments are still proudly setting goals to increase the percentage of energy they get from renewables, and companies continue to advertise their commitments to responsible and sustainable practices.
So, what’s going on? As ESG investing has evolved, several lingering issues have emerged. Some of these issues are internal – they’re a product of how the financial sector has behaved with regards to ESG issues since 2004, while some of them are external and have consequences far beyond the financial markets.
Firstly, and perhaps most importantly, there has been sustained anti-ESG political rhetoric in the United States. Whilst the United States represents the world’s largest equity and fixed-income markets, it has lagged Europe with regards to the adoption and implementation of ESG philosophies. Most notable in the Southern states, this rhetoric has been fuelled mainly by certain media outlets, personalities and politicians, linked with these states’ dependencies on fossil fuel sales for employment and tax revenues. Former Fox News host Tucker Carlson, for example, called ESG “a destructive force pressuring governments to sabotage their own economies”. Under this pressure, somewhat understandably, asset managers in the U.S. have responded by becoming more reserved in their promotion of ESG labelled products.
There have also been incidents of investigations launched into investment managers regarding sustainable investing frameworks and ESG-related shareholder votes. With the U.S. congressional and presidential elections fast approaching in November, this may become even more apparent in 2025, however the same political trends have not been seen to the same extent on this side of the Atlantic so far.
The second factor, however, has very much occurred on this side of the Atlantic. Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in 2022 meant that energy had to be prioritised both as a critical resource and as a hedge against security risk, buoying up the security prices of traditional energy stocks and forcing investment in clean energy to become a secondary concern, hitting the ‘E’ in ESG. While it’s logical that the lack of security with regards to energy imports is a reason to transition towards sustainable resources, rather than away from them, this argument holds primarily in the medium- or long-term. Nations throughout Europe in particular had to react very quickly to an unforeseen shock in the energy markets, leading to a short-term prioritisation of fossil fuels over renewables. This had a knock-on impact on the global sustainable industry, with net flows of global sustainable funds falling from over $150bn in Q4 of 2021 to less than $10bn in Q4 of 2023, before gradually beginning to pick up once again. Global sustainable fund assets now stand at approximately $3trn*.
While both the changing political sentiment in the U.S. and the changes to the energy market are external factors, the third factor has grown out of the financial sector itself, and it’s an issue that the industry has been accused of before: dishonesty. As the pressure has grown on companies and funds alike to behave in accordance with ESG criteria, they have responded by doing everything they can to appear as ‘green’ as possible. Some went too far. Being a relatively new yardstick to measure the performance of companies and funds with, there has been a lot of grey areas in terms of how entities’ ESG credentials are rated and compared to one another. In response to this, we have seen much needed and welcomed regulation be developed both here in the UK, and the EU
‘Greenwashing’, the misleading of investors and consumers by companies to appear more ‘green’ than they really are, has rightly been cracked down on, including through the implementation of the FCA’s Anti-Greenwashing rule. Alongside this, the FCA’s Sustainability Disclosure Requirements (SDR) in the UK are set to bring greater clarity and transparency to sustainable investing, and how firms market ‘sustainable’ products. We welcome these developments.
What’s the future of ESG investing?
We don’t believe that ESG or sustainable investing is just a buzzword or Hype Cycle. Instead, we see it as a core part of a steady, long term transition towards an economy based on technologies, companies and energy sources which help address the most pressing issues humanity faces in the 21st century. This transition will be facilitated in part by governments and international organisations setting goals related to the reduction of climate change. For example, at the UN Climate Change Conference in Azerbaijan this November, one item on the agenda will be the New Collective Quantified Goal (NCQG), under which developed nations commit to provide funds to developing nations specifically to help them combat factors contributing to climate change. Though the specifics have not yet been finalised, this could result in large flows of capital towards ESG-related products and projects in developing markets.
As society, regulation, and the wider economic and environmental backdrop develop, it may be the case that what we currently consider to be ‘ESG’ or ‘sustainable’ investing will one day just be called investing, as all companies become part of the new world in which it’s not possible to thrive without demonstrating social and environmental care. Only time will tell, but for now one thing we can tell you is that the reports of ESG’s death are, indeed, greatly exaggerated.
What does all of this mean for ebi?
As an early adopter of sustainable investing, ebi has long been proud to provide ESG based portfolios for its investors, but we would characterise our philosophy as a holistic, sustainability-focused approach, rather than being limited to environmental, social and governance issues. We do of course, also offer non-ESG screened portfolios for investors who prefer to remove ESG from the equation.
However, as a Discretionary Fund Manager with a passive buy-and-hold philosophy, we don’t react to noise or short-term market trends, and so our approach to ESG and sustainable investing won’t change as a result of the shorter-term issues outlined above.
We look forward to the next decade of sustainable investing, and are focused on pushing the boundaries of the MPS and DFM industries, including the range and depth of sustainability-focused portfolios being offered. This year we launched our Vantage SRI portfolios, which utilise SRI tracker funds managed by Amundi, focused on the top 25% of companies in ESG terms compared to their sector peers, combined with fixed-income funds managed by Northern Trust. We are also in the final stages of launching our Impact portfolio suite, investing in index-tracking impact equity funds, combined with a global green impact fixed income solution.
*Source: Morningstar Global Sustainable Fund Flows: Q2 2024 report
Disclaimer
We do not accept any liability for any loss or damage which is incurred from you acting or not acting as a result of reading any of our publications. You acknowledge that you use the information we provide at your own risk.
Our publications do not offer investment advice and nothing in them should be construed as investment advice. Our publications provide information and education for financial advisers who have the relevant expertise to make investment decisions without advice and is not intended for individual investors.
The information we publish has been obtained from or is based on sources that we believe to be accurate and complete. Where the information consists of pricing or performance data, the data contained therein has been obtained from company reports, financial reporting services, periodicals, and other sources believed reliable. Although reasonable care has been taken, we cannot guarantee the accuracy or completeness of any information we publish. Any opinions that we publish may be wrong and may change at any time. You should always carry out your own independent verification of facts and data before making any investment decisions.
The price of shares and investments and the income derived from them can go down as well as up, and investors may not get back the amount they invested.
Past performance is not necessarily a guide to future performance.

Blog Post by Jonathan Simpson
Investment Support Analyst at ebi Portfolios
What else have we been talking about?
- July Market Review 2025
- Q2 Market Review 2025
- June Market Review 2025
- May Market Review 2025
- Calendar-Based Rebalancing (CBR) vs Tolerance-Based Rebalancing (TBR)




