Tolerance-Based Rebalancing
A Dynamic Portfolio Management Approach for Risk-Adjusted Returns
The importance of Rebalancing
What is it?
Rebalancing is the way in which portfolio asset allocations are managed over time.
Why is it important?
Ensures portfolio alignment with an investor’s target asset allocation and risk tolerance.
What are the benefits?
Rebalancing can potentially have a material impact on returns.
Portfolios are typically designed to align with an investor’s risk tolerance. However, market volatility can cause a portfolio to drift from its intended asset allocation strategy over time. This drift often occurs when riskier assets outperform others, potentially increasing risk beyond what an investor is comfortable with.
Systematic rebalancing is a key component of portfolio risk management, keeping investments aligned with an investor’s risk-adjusted return.
The most common rebalancing approaches are calendar-based, and tolerance-based rebalancing.
Calendar-Based Rebalancing (CBR)
This approach rebalances portfolios at regular fixed date intervals, typically quarterly or annually,
regardless of how much the portfolio has drifted from its target.
Tolerance-Based Rebalancing (TBR)
Tolerance-based rebalancing offers a more disciplined approach to portfolio management, using threshold-based triggers to rebalance when predefined limits are breached.
For example, rebalancing is activated in the Vantage Earth Portfolio 50 if, equity exposure exceeds a 57.6% upper drift threshold or 41.7% lower drift threshold. As shown in the chart below, over three years, calendar-based rebalancing vs. threshold-based rebalancing is compared. Calendar-based rebalancing occurs annually, while tolerance-based rebalancing only activates when portfolio drift exceeds its tolerance band (e.g., 57.6% equity).
How Calendar VS TBR responds to Market Drift
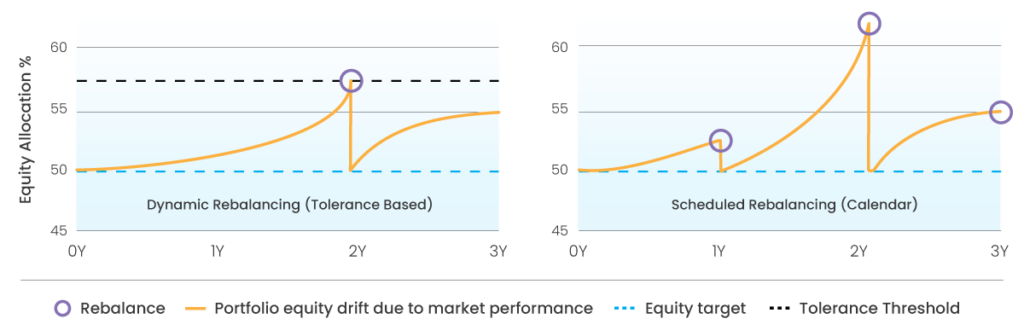
Please note that tolerance-based rebalancing may occur more frequently than calendar-based rebalancing,
depending on market conditions.
Download our ‘What is Tolerance-Based Rebalancing?’ infographic
to learn more
An easy to understand infographic detailing the core principles of Tolerance-Based Rebalancing.
Benefits of Tolerance-Based Rebalancing
Maximise Market Timing
Increases likelihood of capturing
buy-low / sell-high opportunities.
Reduces unnecessary trades
Historically fewer trading events, Reduced implementation burden.
Minimise Market Exposure
Reduces time out of the market.
Resulting in potentially lower expected costs and higher expected returns.
ebi’s view
At ebi, we believe tolerance-based rebalancing strategies may offer demonstrable benefits for long-term investors, ensuring portfolio drift management and risk-adjusted portfolio rebalancing.
Enhanced Performance1: Takes advantage of market opportunities, buying low and selling high.
Real-Time Adjustments: Portfolios stay consistently aligned with clients’ financial goals.
Cost Efficiency: May reduce unnecessary trading activity, lowering transaction costs.
For further details, download our whitepaper, Tolerance Based Rebalancing: Data or Date. In our earlier example, a portfolio with a 50% equity target, TBR would rebalance only if equity allocation moves beyond a 57.6% upper or a 41.7% lower threshold. This dynamic strategy ensures efficient portfolio management without excessive trading.
ebi’s rebalancing Whitepaper – Tolerance Based Rebalancing: Data not Date
ebi’s whitepaper Tolerance-Based Rebalancing: Data not Date is modelled over 30 years of data, analysing portfolio returns with Annual, Quarterly, Tolerance Rebalancing. The model was based on ebi’s Earth portfolio suite and all the calculations include ebi’s 0.12% DIM fee.
Average net rebalancing premium: 0.13%.
Highest net rebalancing premium: 0.28%, Vantage Earth 60.
Consistency: A net rebalancing premium was realised in 9 out of 10 portfolios.
Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results.
What is the Tolerance-Based Rebalancing Premium?
Our research reveals a returns premium advantage of tolerance-based rebalancing over traditional calendar-based approaches. This approach optimises portfolio performance by taking advantage of market dynamics.
Across our Vantage Earth portfolios, we observed an average net rebalancing premium of 0.13%, even after accounting for ebi’s Discretionary Investment Manager (DIM) fee of 0.12%.1
Here’s how it breaks down:
Average net rebalancing premium of 0.13%.
Highest Premiums: The Vantage Earth Earth 60 portfolio demonstrated the greatest benefit, achieving a 0.28% premium.
Consistency: A rebalancing premium was realised in 9 out of 10 portfolios, highlighting the reliability of this strategy across diverse models.
Why It Matters for Clients
By focusing on data-driven threshold-based rebalancing rather than arbitrary dates, tolerance-based rebalancing may improve portfolio risk management and deliver measurable value while maintaining cost efficiency.

Download our ‘Tolerance-Based Rebalancing Whitepaper Pack‘
The pack contains both the Tolerance-Based Investing Whitepaper and condensed Whitepaper Highlights Documents.
Find out More
Discover how ebi’s Tolerance-Based rebalancing strategy can help maintain portfolio alignment, the potential for improving rebalancing impact on portfolio performance, helping mitigate market volatility risks and freeing up an advisers valuable time.
Complete the form to find out more.
Request More Info on Tolerance Based Rebalancing
Disclaimer
This information is intended for financial professionals only. It is not intended for use by, nor should it be distributed to retail clients under any circumstances.
All investments involve risk, and the value of investments may go down as well as up. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results. Always seek professional financial advice.
Please note that tolerance-based rebalancing may occur more frequently than calendar-based rebalancing, depending on market conditions.
1. ebi whitepaper: Tolerance-Based Rebalancing: Data not Date



