
Understanding Behavioural Finance:
Guiding Clients Towards Better Investment Decisions
Learn how emotions and biases can influence financial decisions and how to navigate them to achieve better outcomes for your clients.

Awarded Best
Value for Money 2025

ebi’s Earth Suite Awarded Best
Sustainable/ESG Investment Portfolio 2025

Awarded Best
Outsourced Investment Manager 2025
What is Behavioural Finance?
Behavioural finance explores how psychological factors and cognitive biases can significantly impact investor decision-making.
By understanding these influences, advisers can help clients make more rational and informed choices towards their financial goals.
Jargon Buster: Cognitive Bias
A systematic error in thinking that can significantly impact an investor’s decision-making process, often leading to poor financial outcomes. These mental shortcuts or biases can cause investors to deviate from rational decision-making, leading to irrational or emotional choices.

Download our Behavioural Finance infographic
Behavioural Finance is an area of study that combines psychology,
sociology with economics and finance.
This explains systemic biases that are exhibited by financial markets and investors. It asserts that people often behave irrationally based on emotion and cognitive biases.
Why does behavioural finance matter for advisers?
Identifying & addressing
client biases:
Recognising common pitfalls like sunk cost fallacy, and herd mentality, allows advisers to tailor advice accordingly.
Improving client
communication:
By understanding how clients perceive risk and process information, you can communicate investment strategies more effectively and build stronger relationships.
Enhancing client
outcomes:
Guiding clients towards more rational decisions can help them avoid costly mistakes and achieve their long-term financial objectives.
Common behavioural biases that impact investors
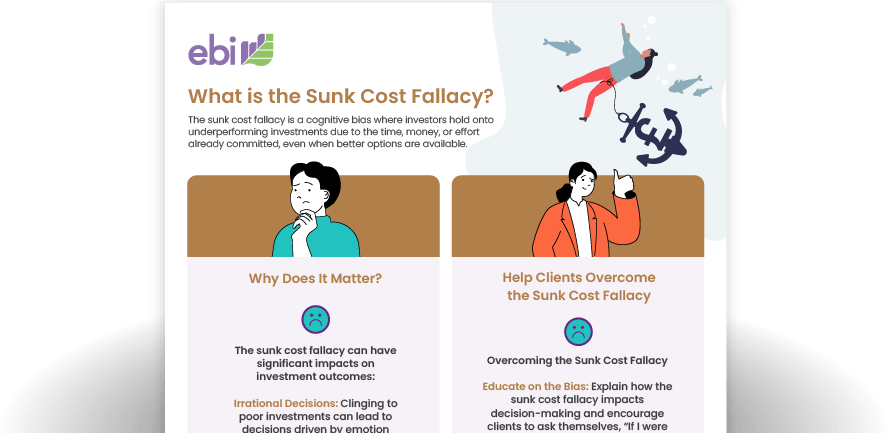
Sunk Cost Fallacy Infographic
The sunk cost fallacy is a cognitive bias where investors hold onto underperforming investments due to the time, money, or effort already committed, even when better options are available.
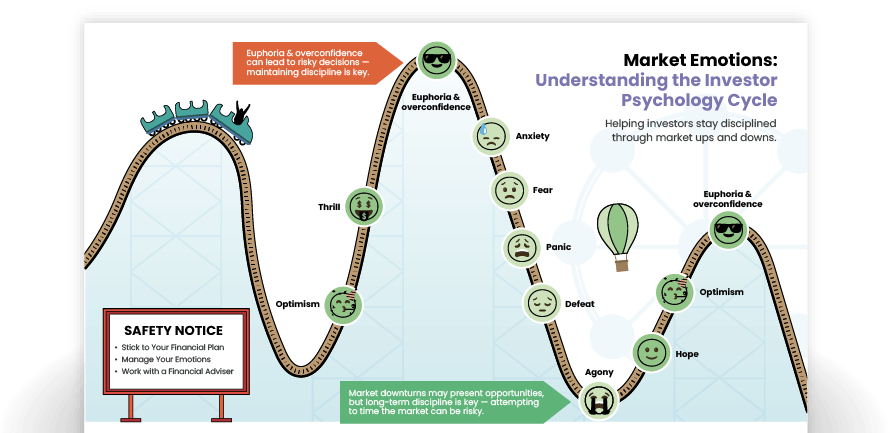
Market Emotions Infographic
Our ‘Market Emotions’ infographic helps investors stay disciplined through market ups and downs.
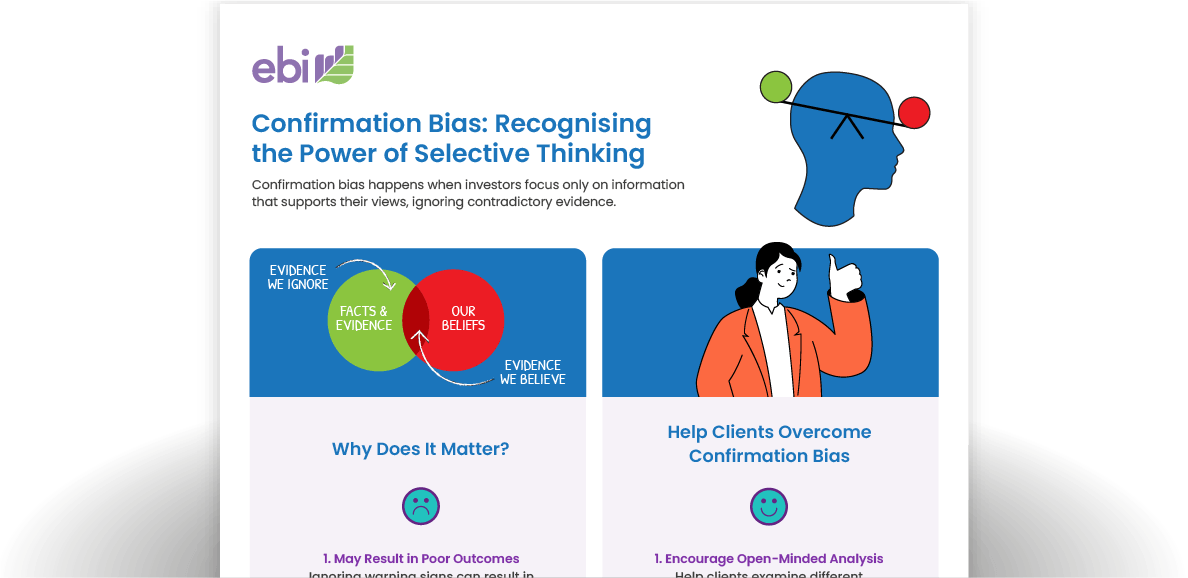
Confirmation Bias Infographic
Confirmation bias is when individuals have an unconscious tendency to look for information that supports their pre-existing beliefs.
Herding Bias Infographic
Herding bias occurs when individuals make decisions based on the actions of others, rather than their independent analysis or research.
Recency Bias Infographic
Recency bias, (also known as availability bias), is when
people give increased weight to more recent events, often ignoring information gathered over a longer time period.
Anchoring Bias Infographic
Anchoring bias is relying heavily on an initial piece of information, the anchor. Subsequent decisions have a bias towards interpreting new information around the anchor.

Self-Serving Bias Infographic
Self-serving bias is the tendency to credit personal skill for positive outcomes while blaming external factors for negative results.
Heuristic Availability Bias Infographic
The availability heuristic is a mental shortcut where decisions are influenced by readily available or recent information, rather than comprehensive analysis.
How to help clients overcome behavioural biases
During periods of market volatility, emotions like fear and greed can easily cloud investor judgment.
Behavioural finance provides a framework for:
Educate Clients on Common Biases:
Help clients understand biases like loss sunk cost fallacy, recency bias, and confirmation bias to empower them to recognise these behaviours in their own decision-making.
Provide Objective Guidance:
Act as a steady voice of reason during market volatility, helping clients avoid emotional decisions driven by fear or greed.
Reinforce Long-Term Strategies:
Encourage clients to stick to their investment plans, reminding them of their long-term goals during periods of market uncertainty.
Build Trust Through Communication:
Regularly communicate with clients, providing reassurance, transparency, and clear explanations to strengthen their confidence in the investment process.
Recognising and addressing behavioural biases can enhance decision-making, but it does not eliminate investment risks. Past performance is not indicative of future results.



